Подготовка окружения#
В данном разделе описан сценарий подготовки окружения для установки DropApp с помощью утилиты Dactl.
Общая схема развертывания представлена на диаграмме:
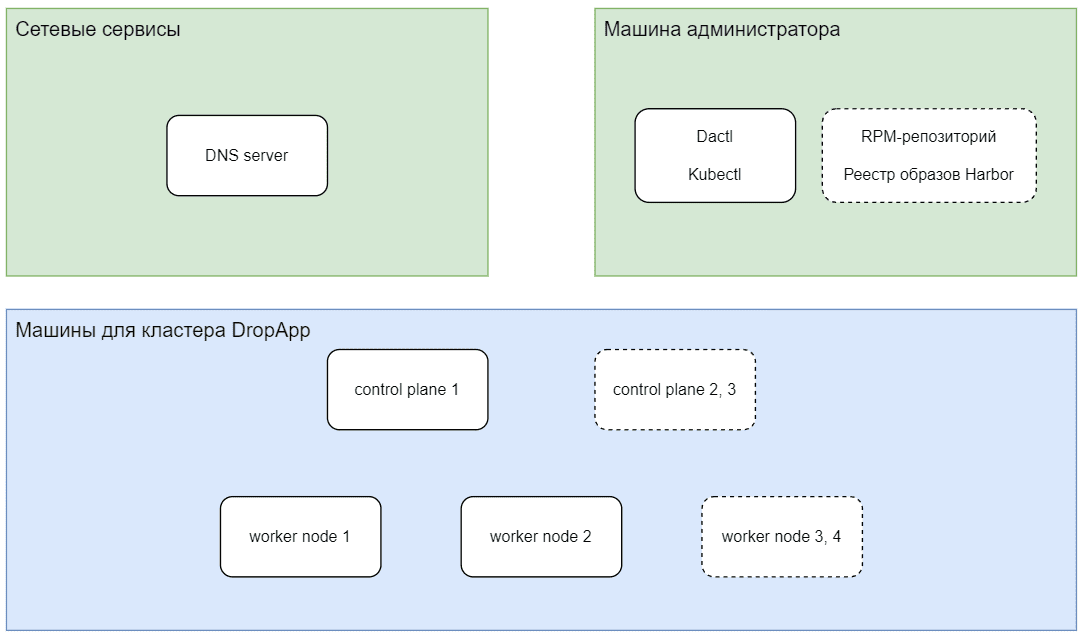
Порядок подготовки к установке:
Предварительные условия#
Примечание
В данной инструкции приведен пример установки реестра образов Harbor и RPM-репозитория на машину администратора
Планирование пула IP-адресов#
DropApp использует балансировщик Metallb для развертывания приложений.
Для использования Metallb зарезервируйте диапазон IP-адресов. Например, 10 адресов из той же подсети, в которой развернуты серверы для установки DropApp.
DNS#
Зарегистрируйте в DNS записи для приложений. Формат записей hostname: <tool>.<clusteName>.<domain>. Примеры указаны в таблице ниже.
Приложение |
Пример записи |
IP-адрес |
|---|---|---|
Console |
|
Первый из пула адресов для Metallb |
Dex |
|
Первый из пула адресов для Metallb |
Другие сервисы |
|
Первый из пула адресов для Metallb |
Control plane кластера |
|
Адреса машин для control plane |
Worker nodes кластера |
|
Адреса машин для worker nodes |
Реестр |
|
Адрес реестра |
Имена должны разрешаться c nodes кластера.
Машина администратора#
DropApp настраивается администратором на виртуальной машине с предустановленной ОС.
Для установки требуется машина администратора кластера с которой будет запускаться утилита Dactl.
Машина администратора кластера должна быть в одном сетевом контуре с:
будущими nodes кластера;
image registry (реестром образов), куда будут загружены образы контейнеров DropApp;
RPM-репозиторием.
Загрузка дистрибутивов из личного кабинета#
Примечание
Дальнейшие действия выполняются из каталога /root.
Загрузите следующие дистрибутивы продукта и компонента Управляющий слой из Личного Кабинета клиента:
архив продукта:
K8S-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip;архив управляющего слоя:
K8S-mgmt-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip.
Распаковка дистрибутивов#
Важно
Архив продукта имеет большой размер - более 10 Гб, рекомендуется перед разархивацией установить переменную окружения UNZIP_DISABLE_ZIPBOMB_DETECTION=TRUE с помощью команды:
export UNZIP_DISABLE_ZIPBOMB_DETECTION=TRUE
Для получения вложенных архивов и файлов:
Разархивируйте из архива
K8S-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zipвложенный архивK8S-k8sc-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip:unzip K8S-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zipРазархивируйте из архива
K8S-k8sc-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zipвложенные архивы с образами и RPM-пакетами дистрибутива:unzip K8S-k8sc-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zipРазархивируйте архивы с образами и RPM-пакетами:
unzip k8sc-images-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip -d images unzip k8sc-rpms-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip -d rpms unzip rpms/K8S-k8sc-rpms-<version>-<distrib_number>-SBEL9-distrib.zip -d rpms/rpms-sbel9 unzip rpms/K8S-k8sc-rpms-<version>-<distrib_number>-SBEL8-distrib.zip -d rpms/rpms-sbel8Разархивируйте архив с утилитой Dactl:
unzip K8S-mgmt-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip -d mgmtРазархивируйте образы и бинарный файл
dactl:unzip ./mgmt/mgmt-binaries-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip -d ./dactl unzip ./dactl/package/bh/dactl-<version>.zip -d ./dactl/ unzip ./mgmt/mgmt-images-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip -d ./images-mgmtПроверьте версию Dactl:
./dactl/dactl versionПример вывода:
Platform V DropApp version: <version>
Подготовка артефактов DropApp#
Примечание
При наличии реестра образов и RPM-репозитория перейдите к разделу Загрузка образов DropApp в реестр.
Подготовка артефактов включает в себя создание реестра образов для контейнеров и RPM-репозитория. Шаги инструкции, приведенной ниже, выполняются последовательно.
Создание реестра образов#
Для установки DropApp необходим реестр образов контейнеров Harbor. В данном разделе описан процесс создания реестра образов .
Предварительные условия для установки реестра образов#
Для установки реестра образов Harbor необходимо выполнить предварительные условия:
установлен Podman-Compose;
dnf install python3-pip -y pip3 install podman-composeотключен
selinux:setenforce 0Примечание
Для постоянного отключения SElinux необходимо отредактировать конфигурационный файл
selinux:vi /etc/selinux/configSELINUX=permissiveприсутствует доступ в интернет;
Машина администратора, для которой должны быть выполнены следующие условия:
у пользователя в системе должны быть административные полномочия (root или аналогичные);
машина должна быть в одном сетевом контуре с будущими nodes кластера;
на машине должны быть установлены Docker или Podman.
Дистрибутив
K8S-<version>-<distrib_number>-distrib.zip;DNS-запись вида
registry.da-cluster.<public_domain>с адресом текущей машины.
Примечание
Инструмент Podman входит в состав продукта OC Platform V SberLinux OS Server (далее – SberLinux).
Минимальная конфигурация машины для реестра образов и RPM-репозитория приведена в таблице.
Значение |
Размер |
|---|---|
ЦПУ [CPU] (в ядрах) |
4 (с поддержкой VT*) |
ОЗУ [RAM] |
8192 Мб |
Размер диска [HDD/SSD] |
150 Гб |
Генерация сертификатов для реестра образов#
В качестве доверенных сертификатов можно использовать уже имеющиеся в системе. Если их нет, то создайте для реестра самоподписные сертификаты, следуя сценарию ниже:
Создайте каталог
harborи перейдите в него.Создайте в каталоге
harborскриптharbor_certs.sh.harbor_certs.sh
#!/bin/bash set -e # Парсинг аргументов while [[ "$#" -gt 0 ]]; do case $1 in --ip) IP="$2"; shift ;; --hostname) HOSTNAME="$2"; shift ;; --passphrase) PASSPHRASE="$2"; shift ;; --container-engine) CONTAINER_ENGINE="$2"; shift ;; *) echo "Unknown parameter passed: $1"; exit 1 ;; esac shift done # Если IP не передан, используйте первый IP из вывода hostname -I if [ -z "$IP" ]; then IP=$(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}') fi # Если HOSTNAME не передан, используйте текущий hostname if [ -z "$HOSTNAME" ]; then HOSTNAME=$(hostname) fi if [ -z "$CONTAINER_ENGINE" ]; then CONTAINER_ENGINE="podman" fi # Создайте директорию certs, если она существует, удалите ее if [ -d "./certs" ]; then rm -rf ./certs fi mkdir ./certs # Генерация корневого ключа и сертификата openssl genrsa -out ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.key 4096 if [ -z "$PASSPHRASE" ]; then openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.key -sha512 -days 3650 -out ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.crt -subj "/C=RU/L=Moscow/O=Platform V DropApp/CN=dropapp_internal_ca" else openssl req -x509 -new -key ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.key -sha512 -days 3650 -out ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.crt -subj "/C=RU/L=Moscow/O=Platform V DropApp/CN=dropapp_internal_ca" -passin pass:"$PASSPHRASE" fi # Генерация ключа для сертификата приложения openssl genrsa -out ./certs/harbor.key 4096 # Создание конфигурационного файла для расширений сертификата cat > ./certs/v3.ext <<-EOF authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer basicConstraints=CA:FALSE keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment subjectAltName = @alt_names [alt_names] IP.1 = $IP DNS.1 = $HOSTNAME DNS.2 = portal DNS.3 = core DNS.4 = registry DNS.5 = job_service DNS.6 = trivy_adapter DNS.7 = harbor_db DNS.8 = redis DNS.9 = registryctl DNS.8 = proxy EOF # Генерация CSR для сертификата приложения openssl req -new -key ./certs/harbor.key -out ./certs/harbor.csr -subj "/C=RU/L=Moscow/O=Platform V DropApp/CN=$HOSTNAME" # Подписание сертификата приложения корневым сертификатом if [ -z "$PASSPHRASE" ]; then openssl x509 -req -in ./certs/harbor.csr -CA ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.crt -CAkey ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.key -CAcreateserial -out ./certs/harbor.crt -days 3650 -sha512 -extfile ./certs/v3.ext else openssl x509 -req -in ./certs/harbor.csr -CA ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.crt -CAkey ./certs/harbor_internal_ca.key -CAcreateserial -out ./certs/harbor.crt -days 3650 -sha512 -extfile ./certs/v3.ext -passin pass:"$PASSPHRASE" fi for NAME in portal core registry job_service trivy_adapter harbor_db redis proxy registryctl; do cp ./certs/harbor.crt "./certs/${NAME}.crt" cp ./certs/harbor.key "./certs/${NAME}.key" done echo "Сертификаты успешно созданы в директории ./certs" echo "Скопируйте harbor.crt в директорию /etc/containers/certs.d/$HOSTNAME" sudo rm -rf /etc/containers/certs.d/$HOSTNAME sudo mkdir -p /etc/containers/certs.d/$HOSTNAME sudo cp ./certs/harbor.crt /etc/containers/certs.d/$HOSTNAME/ca.crt # Условие для container-engine if [[ "$CONTAINER_ENGINE" == "docker" ]]; then echo "Скопируйте harbor.crt в директорию /etc/docker/certs.d/$HOSTNAME" sudo rm -rf /etc/docker/certs.d/$HOSTNAME sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker/certs.d/$HOSTNAME sudo cp ./certs/harbor.crt /etc/docker/certs.d/$HOSTNAME/ca.crt sudo systemctl restart docker fi if [[ "$CONTAINER_ENGINE" == "podman" ]]; then sudo systemctl restart podman fiПараметры скрипта, используемые в команде, приведены в разделе ниже.
Сделайте файл исполняемым:
chmod +x harbor_certs.shЗапустите скрипт, он сгенерирует самоподписанные сертификаты для реестра и расположит их в каталоге
certs.dдляcontainer runtime:./harbor_certs.sh --hostname registry.da-cluster.domain.ru --container-engine <docker|podman>
Параметры скрипта#
Параметры скрипта harbor_certs.sh:
--ip- опциональный параметр, по умолчанию равен выводуhostname -I, то есть публичному IP текущей машины;--hostname- обязательный параметр, сертификат будет выписан на этот hostname;--passphrase- опциональный параметр для пароля сертификата;--container-engine- опциональный параметр, можно передатьdockerилиpodman, по умолчаниюpodman.
Важно
Для создаваемого реестра образов должна быть DNS запись.
Установка реестра образов#
Для установки реестра образов выполните:
Создайте в каталоге
harborфайлharbor.yml:harbor.yml
# Configuration file of Harbor # The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service. # DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients. hostname: harbor.bootstrap.domain.ru # http related config http: # port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port # port: 80 # https related config https: # https port for harbor, default is 443 port: 443 # The path of cert and key files for nginx certificate: /home/user/harbor/certs/harbor.crt private_key: /home/user/harbor/certs/harbor.key # # Uncomment following will enable tls communication between all harbor components #internal_tls: # # set enabled to true means internal tls is enabled # enabled: true # # put your cert and key files on dir # dir: /root/harbor/certs # # enable strong ssl ciphers (default: false) # strong_ssl_ciphers: false # Uncomment external_url if you want to enable external proxy # And when it enabled the hostname will no longer used # external_url: https://reg.mydomain.com:8433 # The initial password of Harbor admin # It only works in first time to install harbor # Remember Change the admin password from UI after launching Harbor. harbor_admin_password: <harbor-admin-password> # Harbor DB configuration database: # The password for the root user of Harbor DB. Change this before any production use. password: root123 # The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool. If it <=0, no idle connections are retained. max_idle_conns: 100 # The maximum number of open connections to the database. If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections. # Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for postgres of harbor. max_open_conns: 900 # The maximum amount of time a connection may be reused. Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse. If it <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's age. # The value is a duration string. A duration string is a possibly signed sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as "300ms", "-1.5h" or "2h45m". Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h". conn_max_lifetime: 5m # The maximum amount of time a connection may be idle. Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse. If it <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's idle time. # The value is a duration string. A duration string is a possibly signed sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as "300ms", "-1.5h" or "2h45m". Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h". conn_max_idle_time: 0 # The default data volume data_volume: ./data_harbor # Harbor Storage settings by default is using /data dir on local filesystem # Uncomment storage_service setting If you want to using external storage # storage_service: # # ca_bundle is the path to the custom root ca certificate, which will be injected into the truststore # # of registry's containers. This is usually needed when the user hosts a internal storage with self signed certificate. # ca_bundle: # # storage backend, default is filesystem, options include filesystem, azure, gcs, s3, swift and oss # # for more info about this configuration please refer https://docs.docker.com/registry/configuration/ # filesystem: # maxthreads: 100 # # set disable to true when you want to disable registry redirect # redirect: # disable: false # Trivy configuration # # Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases. # It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached # in the local file system. In addition, the database contains the update timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it # should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one. Currently, the database is updated every # 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub. trivy: # ignoreUnfixed The flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities ignore_unfixed: false # skipUpdate The flag to enable or disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub # # You might want to enable this flag in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues. # If the flag is enabled you have to download the `trivy-offline.tar.gz` archive manually, extract `trivy.db` and # `metadata.json` files and mount them in the `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db` path. skip_update: false # # skipJavaDBUpdate If the flag is enabled you have to manually download the `trivy-java.db` file and mount it in the # `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/java-db/trivy-java.db` path skip_java_db_update: false # # The offline_scan option prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies. # Scanning JAR files and pom.xml may require Internet access for better detection, but this option tries to avoid it. # For example, the offline mode will not try to resolve transitive dependencies in pom.xml when the dependency doesn't # exist in the local repositories. It means a number of detected vulnerabilities might be fewer in offline mode. # It would work if all the dependencies are in local. # This option doesn't affect DB download. You need to specify "skip-update" as well as "offline-scan" in an air-gapped environment. offline_scan: false # # Comma-separated list of what security issues to detect. Possible values are `vuln`, `config` and `secret`. Defaults to `vuln`. security_check: vuln # # insecure The flag to skip verifying registry certificate insecure: true # github_token The GitHub access token to download Trivy DB # # Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough # for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000 # requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult # https://docs.github.com/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#rate-limiting # # You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in # https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line # # github_token: xxx jobservice: # Maximum number of job workers in job service max_job_workers: 10 # The jobLoggers backend name, only support "STD_OUTPUT", "FILE" and/or "DB" job_loggers: - STD_OUTPUT - FILE # - DB # The jobLogger sweeper duration (ignored if `jobLogger` is `stdout`) logger_sweeper_duration: 1 #days notification: # Maximum retry count for webhook job webhook_job_max_retry: 3 # HTTP client timeout for webhook job webhook_job_http_client_timeout: 3 #seconds # Log configurations log: # options are debug, info, warning, error, fatal level: info # configs for logs in local storage local: # Log files are rotated log_rotate_count times before being removed. If count is 0, old versions are removed rather than rotated. rotate_count: 50 # Log files are rotated only if they grow bigger than log_rotate_size bytes. If size is followed by k, the size is assumed to be in kilobytes. # If the M is used, the size is in megabytes, and if G is used, the size is in gigabytes. So size 100, size 100k, size 100M and size 100G # are all valid. rotate_size: 200M # The directory on your host that store log location: /var/log/harbor # Uncomment following lines to enable external syslog endpoint. # external_endpoint: # # protocol used to transmit log to external endpoint, options is tcp or udp # protocol: tcp # # The host of external endpoint # host: localhost # # Port of external endpoint # port: 5140 #This attribute is for migrator to detect the version of the .cfg file, DO NOT MODIFY! _version: 2.9.0 # Uncomment external_database if using external database. # external_database: # harbor: # host: harbor_db_host # port: harbor_db_port # db_name: harbor_db_name # username: harbor_db_username # password: harbor_db_password # ssl_mode: disable # max_idle_conns: 2 # max_open_conns: 0 # Uncomment redis if need to customize redis db # redis: # # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable # # registry_db_index: 1 # # jobservice_db_index: 2 # # trivy_db_index: 5 # # it's optional, the db for harbor business misc, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it. # # harbor_db_index: 6 # # it's optional, the db for harbor cache layer, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it. # # cache_db_index: 7 # Uncomment redis if need to customize redis db # redis: # # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable # # registry_db_index: 1 # # jobservice_db_index: 2 # # trivy_db_index: 5 # # it's optional, the db for harbor business misc, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it. # # harbor_db_index: 6 # # it's optional, the db for harbor cache layer, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it. # # cache_layer_db_index: 7 # Uncomment external_redis if using external Redis server # external_redis: # # support redis, redis+sentinel # # host for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis> # # host for redis+sentinel: # # <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3> # host: redis:6379 # password: # # Redis AUTH command was extended in Redis 6, it is possible to use it in the two-arguments AUTH <username> <password> form. # # there's a known issue when using external redis username ref:https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/18892 # # if you care about the image pull/push performance, please refer to this https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/wiki/Harbor-FAQs#external-redis-username-password-usage # # username: # # sentinel_master_set must be set to support redis+sentinel # #sentinel_master_set: # # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable # registry_db_index: 1 # jobservice_db_index: 2 # trivy_db_index: 5 # idle_timeout_seconds: 30 # # it's optional, the db for harbor business misc, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it. # # harbor_db_index: 6 # # it's optional, the db for harbor cache layer, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it. # # cache_layer_db_index: 7 # Uncomment uaa for trusting the certificate of uaa instance that is hosted via self-signed cert. # uaa: # ca_file: /path/to/ca # Global proxy # Config http proxy for components, e.g. http://my.proxy.com:3128 # Components doesn't need to connect to each others via http proxy. # Remove component from `components` array if want disable proxy # for it. If you want use proxy for replication, MUST enable proxy # for core and jobservice, and set `http_proxy` and `https_proxy`. # Add domain to the `no_proxy` field, when you want disable proxy # for some special registry. proxy: http_proxy: https_proxy: no_proxy: components: - core - jobservice - trivy # metric: # enabled: false # port: 9090 # path: /metrics # Trace related config # only can enable one trace provider(jaeger or otel) at the same time, # and when using jaeger as provider, can only enable it with agent mode or collector mode. # if using jaeger collector mode, uncomment endpoint and uncomment username, password if needed # if using jaeger agetn mode uncomment agent_host and agent_port # trace: # enabled: true # # set sample_rate to 1 if you wanna sampling 100% of trace data; set 0.5 if you wanna sampling 50% of trace data, and so forth # sample_rate: 1 # # # namespace used to differenciate different harbor services # # namespace: # # # attributes is a key value dict contains user defined attributes used to initialize trace provider # # attributes: # # application: harbor # # # jaeger should be 1.26 or newer. # # jaeger: # # endpoint: http://hostname:14268/api/traces # # username: # # password: # # agent_host: hostname # # # export trace data by jaeger.thrift in compact mode # # agent_port: 6831 # # otel: # # endpoint: hostname:4318 # # url_path: /v1/traces # # compression: false # # insecure: true # # # timeout is in seconds # # timeout: 10 # Enable purge _upload directories upload_purging: enabled: true # remove files in _upload directories which exist for a period of time, default is one week. age: 168h # the interval of the purge operations interval: 24h dryrun: false # Cache layer configurations # If this feature enabled, harbor will cache the resource # `project/project_metadata/repository/artifact/manifest` in the redis # which can especially help to improve the performance of high concurrent # manifest pulling. # NOTICE # If you are deploying Harbor in HA mode, make sure that all the harbor # instances have the same behaviour, all with caching enabled or disabled, # otherwise it can lead to potential data inconsistency. cache: # not enabled by default enabled: false # keep cache for one day by default expire_hours: 24 # Harbor core configurations # Uncomment to enable the following harbor core related configuration items. # core: # # The provider for updating project quota(usage), there are 2 options, redis or db, # # by default is implemented by db but you can switch the updation via redis which # # can improve the performance of high concurrent pushing to the same project, # # and reduce the database connections spike and occupies. # # By redis will bring up some delay for quota usage updation for display, so only # # suggest switch provider to redis if you were ran into the db connections spike aroud # # the scenario of high concurrent pushing to same project, no improvment for other scenes. # quota_update_provider: redis # Or dbОтредактируйте файл
harbor.yml:заполните
hostnameкорректным адресом, для которого были сгенерированы сертификаты в разделе Генерация сертификатов для реестра образов выше;в секции
httpsзаполните полный путь до каталогаcerts, которая была создана скриптомharbor_certs.shиз шага 3 в разделе Генерация сертификатов для реестра образов выше, для полейcertificateиprivate_key;поменяйте преднастроенный пароль администратора (по умолчанию
<harbor-admin-password>).
Создайте в каталоге
harborскриптharbor_registry_install.sh:harbor_registry_install.sh
#!/bin/bash set -e CONTAINER_ENGINE="podman" while [[ "$#" -gt 0 ]]; do case $1 in --container-engine) if [[ -n "$2" ]]; then CONTAINER_ENGINE="$2" shift else echo "Ошибка: Для --container-engine не указано значение." exit 1 fi ;; *) echo "Неизвестный параметр: $1" exit 1 ;; esac shift done if ! command -v "$CONTAINER_ENGINE" &> /dev/null; then echo "Ошибка: Команда '$CONTAINER_ENGINE' не найдена. Убедитесь, что она установлена." exit 1 fi echo "Используется контейнерный движок: $CONTAINER_ENGINE" if [[ -n "$HARBOR_BUNDLE_DIR" ]]; then harbor_prepare_path=$HARBOR_BUNDLE_DIR else harbor_prepare_path="$( cd "$(dirname "$0")" ; pwd -P )" fi echo "Подготовительный каталог: ${harbor_prepare_path}" rm -rf ${harbor_prepare_path}/input mkdir -p ${harbor_prepare_path}/input input_dir=${harbor_prepare_path}/input if [[ ! "$1" =~ ^\-\- ]] && [ -f "$1" ] then cp $1 $input_dir/harbor.yml shift else if [ -f "${harbor_prepare_path}/harbor.yml" ];then cp ${harbor_prepare_path}/harbor.yml $input_dir/harbor.yml else echo "Не найден конфигурационный файл ${harbor_prepare_path}/harbor.yml" exit 1 fi fi data_path=$(grep '^[^#]*data_volume:' $input_dir/harbor.yml | awk '{print $NF}') echo "Каталог с данными: ${data_path}" mkdir -p $data_path previous_secretkey_path=/data/secretkey previous_defaultalias_path=/data/defaultalias if [ -f $previous_secretkey_path ]; then mkdir -p $data_path/secret/keys mv $previous_secretkey_path $data_path/secret/keys fi if [ -f $previous_defaultalias_path ]; then mkdir -p $data_path/secret/keys mv $previous_defaultalias_path $data_path/secret/keys fi secret_dir=${data_path}/secret config_dir=$harbor_prepare_path/common/config mkdir -p $secret_dir mkdir -p $config_dir $CONTAINER_ENGINE run --rm -v $input_dir:/input \ -v $data_path:/data \ -v $harbor_prepare_path:/compose_location \ -v $config_dir:/config \ -v /:/hostfs \ --privileged \ docker.io/goharbor/prepare:v2.9.3 prepare echo "Удаление подготовительного каталога" rm -rf ${harbor_prepare_path}/input sed -i 's|goharbor|docker.io/goharbor|g' docker-compose.yml sed -i 's|"syslog"|"journald"|g' docker-compose.yml sed -i '/syslog-address:/d' docker-compose.yml sudo chmod -R 777 ./data_harbor/database sudo chmod -R 777 ./data_harbor/redis mkdir ${data_path}/cert sudo cp certs/* ${data_path}/cert/ sudo chown -R 10000:10000 ${data_path}/cert/ sudo chmod -R 777 ${data_path}/cert/ echo "Запуск Harbor" #sudo podman-compose up -dСделайте файл исполняемым:
chmod +x harbor_registry_install.shУстановите реестр образов, запустив скрипт
harbor_registry_install.sh:./harbor_registry_install.sh --container-engine <docker|podman>Для запуска реестра образов выполните команду:
<docker|podman>-compose up -dДля настройки автозапуска Harbor создайте системную службу
harbor.service:vi /etc/systemd/system/harbor.serviceПример настройки:
[Unit] Description=harbor After=network.target [Service] Type=oneshot RemainAfterExit=yes ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/podman-compose -f /root/harbor/docker-compose.yml up -d ExecStop=/usr/local/bin/podman-compose -f /root/harbor/docker-compose.yml down Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=default.target/root/harbor/docker-compose.yml- пример пути расположения файлаdocker-compose.yml. При необходимости укажите иной каталог для установки.Добавьте службу в автозапуск с помощью последовательности команд:
активируйте службу
harbor.service:
systemctl enable harbor.serviceперезагрузите демоны:
systemctl daemon-reloadзапустите службу
harbor.service:
systemctl start harbor.serviceПроверьте состояние службы:
systemctl status harbor.serviceПример вывода команды:
● harbor.service - harbor Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/harbor.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (exited) since Fri 2025-04-25 11:53:57 MSK; 2min 6s ago Process: 833 ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/podman-compose -f /root/harbor/docker-compose.yml up -d (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 833 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Валидация установки реестра образов#
Выполните sudo <docker|podman> compose ps и убедитесь, что все контейнеры запущены, рестартов нет:
<docker|podman> compose ps
Пользовательский интерфейс Harbor будет доступен в браузере по адресу, который был указан в harbor.yml, например https://registry.da-cluster.domain.ru.
Создание проекта для образов#
Зайдите в пользовательский интерфейс Harbor под учетной записью администратора и создайте проект
dapp: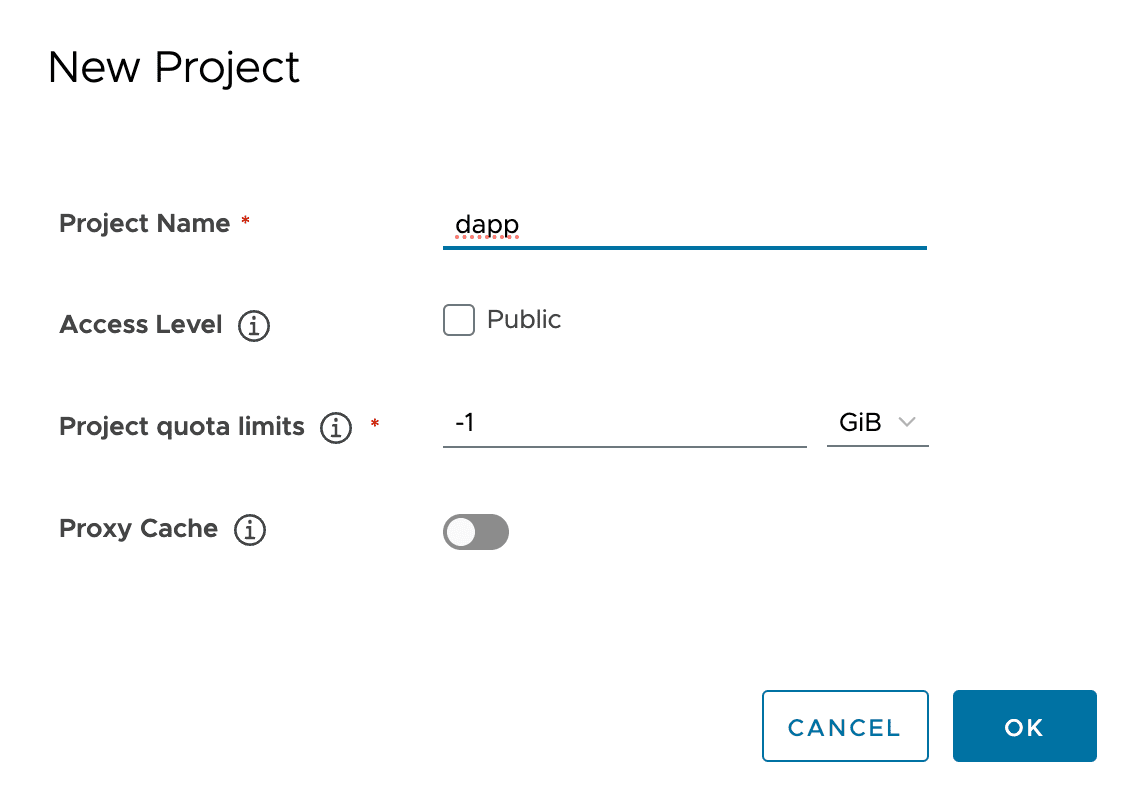
Выполните вход в созданный реестр. Логин (
Username) - этоadmin, пароль установлен вharbor.yml, полеharbor_admin_password:podman login harbor.bootstrap.domain.ru Username: admin Password: Login Succeeded!
Создание RPM-репозитория#
Пакеты DropApp#
Важно
selinux должен быть отключен командой sudo setenforce 0.
В разделе Распаковка дистрибутивов был распакован архив с RPM-репозиторием и получены два каталога с пакетами DropApp собранными для SberLinux 8 и 9 поколения:
rpms/K8S-k8sc-rpms-<version>-<distrib_number>-SBEL9-distrib.zip;rpms/K8S-k8sc-rpms-<version>-<distrib_number>-SBEL8-distrib.zip.
Для создания RPM-репозитория выполните следующие шаги:
Создайте файл
rpm_repo_install.sh:rpm_repo_install.sh
#!/bin/bash # Проверка прав доступа if [[ $EUID -ne 0 ]]; then echo "Этот скрипт должен быть запущен с правами root (sudo)." exit 1 fi # Функция вывода справки usage() { echo "Использование: $0 --src-dir <путь_к_каталогу_с_RPM_пакетами> --dest-dir <внутренний_каталог>" exit 1 } # Проверка состояния SELinux if [[ $(getenforce) == "Enabled" ]]; then echo "SELinux включен. Предварительно выключите SELinux." exit 1 fi # Парсинг параметров while [[ "$#" -gt 0 ]]; do case $1 in --src-dir) src_dir="$2" shift ;; --dest-dir) dest_dir="$2" shift ;; *) echo "Неизвестный параметр: $1" usage ;; esac shift done # Проверка наличия обязательных параметров if [[ -z "$src_dir" || -z "$dest_dir" ]]; then usage fi # Проверка существования исходного каталога с RPM пакетами if [[ ! -d "$src_dir" ]]; then echo "Указанный исходный каталог не существует: $src_dir" exit 1 fi # Создание целевого каталога внутри репозитория repo_root="/usr/share/nginx/html" repo_dest_dir="$repo_root/$dest_dir" echo "Создание целевого каталога: $repo_dest_dir..." mkdir -p "$repo_dest_dir" # Копирование RPM пакетов в целевой каталог echo "Копирование RPM пакетов из $src_dir в $repo_dest_dir..." cp -r "$src_dir"/* "$repo_dest_dir/" # Установка необходимых пакетов echo "Установка необходимых пакетов..." yum install -y createrepo nginx # Создание RPM репозитория echo "Создание RPM репозитория в каталоге: $repo_dest_dir..." createrepo "$repo_dest_dir" # Настройка Nginx для работы на порту 8080 echo "Настройка Nginx..." cat <<EOF > /etc/nginx/nginx.conf user nginx; worker_processes auto; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; pid /run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; server { listen 8080; server_name localhost; location / { root $repo_root; autoindex on; autoindex_exact_size off; } } } EOF # Запуск и включение автозапуска Nginx echo "Запуск Nginx..." systemctl start nginx systemctl enable nginx # Открытие порта 8080 в файрволе (только если firewalld запущен) if systemctl is-active --quiet firewalld; then echo "Открытие порта 8080 в файрволе..." firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload else echo "Firewalld не запущен. Пропустить настройку firewall." fi # Получение IP-адреса сервера server_ip=$(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}') if [[ -z "$server_ip" ]]; then echo "Не удалось определить IP-адрес сервера." exit 1 fi # Вывод инструкций по настройке .repo файла echo "RPM репозиторий успешно создан и доступен по адресу:" echo "http://$server_ip:8080/$dest_dir/" echo "" echo "Добавьте следующий блок в ваш .repo файл:" echo "" cat <<EOF [$dest_dir] name=$dest_dir Repository baseurl=http://$server_ip:8080/$dest_dir enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 EOFВажно
Скрипт устанавливает пакеты
createrepoиnginx, доступные в репозиториях SberLinux.Сделайте файл исполняемым:
chmod +x rpm_repo_install.shЗапустите скрипт, передав ему путь до разархивированного каталога:
./rpm_repo_install.sh --src-dir ./rpms/rpms-sbel9 --dest-dir "dapp-<version>-sbel9"
Пакеты SberLinux#
Пакеты DropApp имеют зависимости от пакетов из репозиториев SberLinux, поэтому необходимо добавить репозиторий SberLinux в онлайн-репозиторий, который был создан в разделе Пакеты DropApp выше.
Для этого выполните следующие шаги:
Скачайте из репозиториев SberLinux ISO-файл и смонтируйте его на машине администратора:
mkdir /mnt/disk mount -t iso9660 /dev/sr0 /mnt/diskСкопируйте репозитории BaseOS и AppStream в созданный RPM-репозиторий, используя скрипт
rpm_repo_install.sh:./rpm_repo_install.sh --src-dir /mnt/disk/BaseOS --dest-dir sbel-<version>-baseos ./rpm_repo_install.sh --src-dir /mnt/disk/AppStream --dest-dir sbel-<version>-appstream
После выполнения шагов репозитории DropApp и SberLinux доступны по адресам:
http://<ip-address-rpm-repo>:8080/dapp-<version>-sbel9;http://<ip-address-rpm-repo>:8080/sbel-<version>-baseos.
Загрузка образов DropApp в реестр#
Dactl при загрузке образов использует утилиту skopeo.
Установите skopeo, например, следующей командой:
dnf install skopeo
Примечание
Инструмент skopeo входит в состав продукта SberLinux.
Образы MGMT#
Загрузите образы из каталога images_mgmt в созданный реестр, используя Dactl:
./dactl/dactl copy images --src ./images-mgmt --dest registry.da-cluster.domain.ru/dapp
Образы K8SC#
Загрузите образы из каталога images_mgmt в созданный реестр, используя Dactl:
./dactl/dactl copy images --src ./images --dest registry.da-cluster.domain.ru/dapp
Результат подготовки окружения#
Результатом подготовки окружения является:
настроенные DNS-записи;
выделенные IP-адреса;
реестр образов Harbor;
RPM-репозиторий.
Примечание
Дальнейшая настройка и установка кластера DropApp производится с этой машины